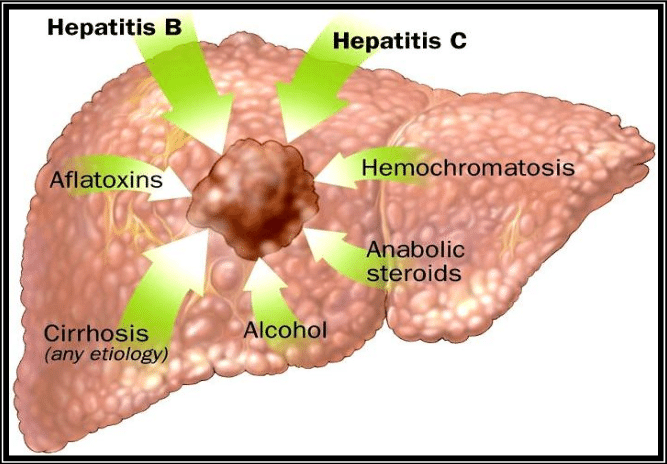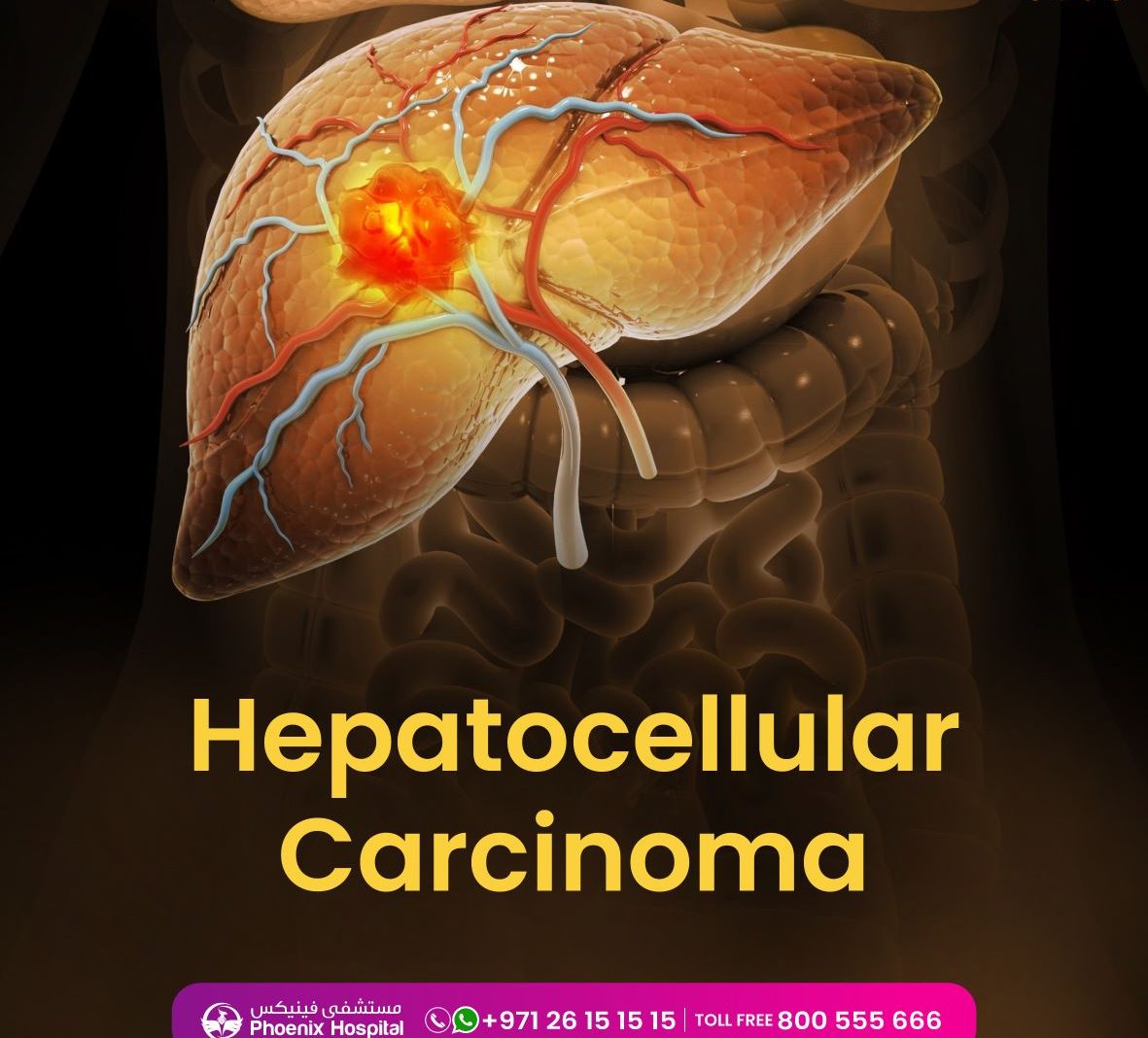
HCC – Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Symptoms, Treatments
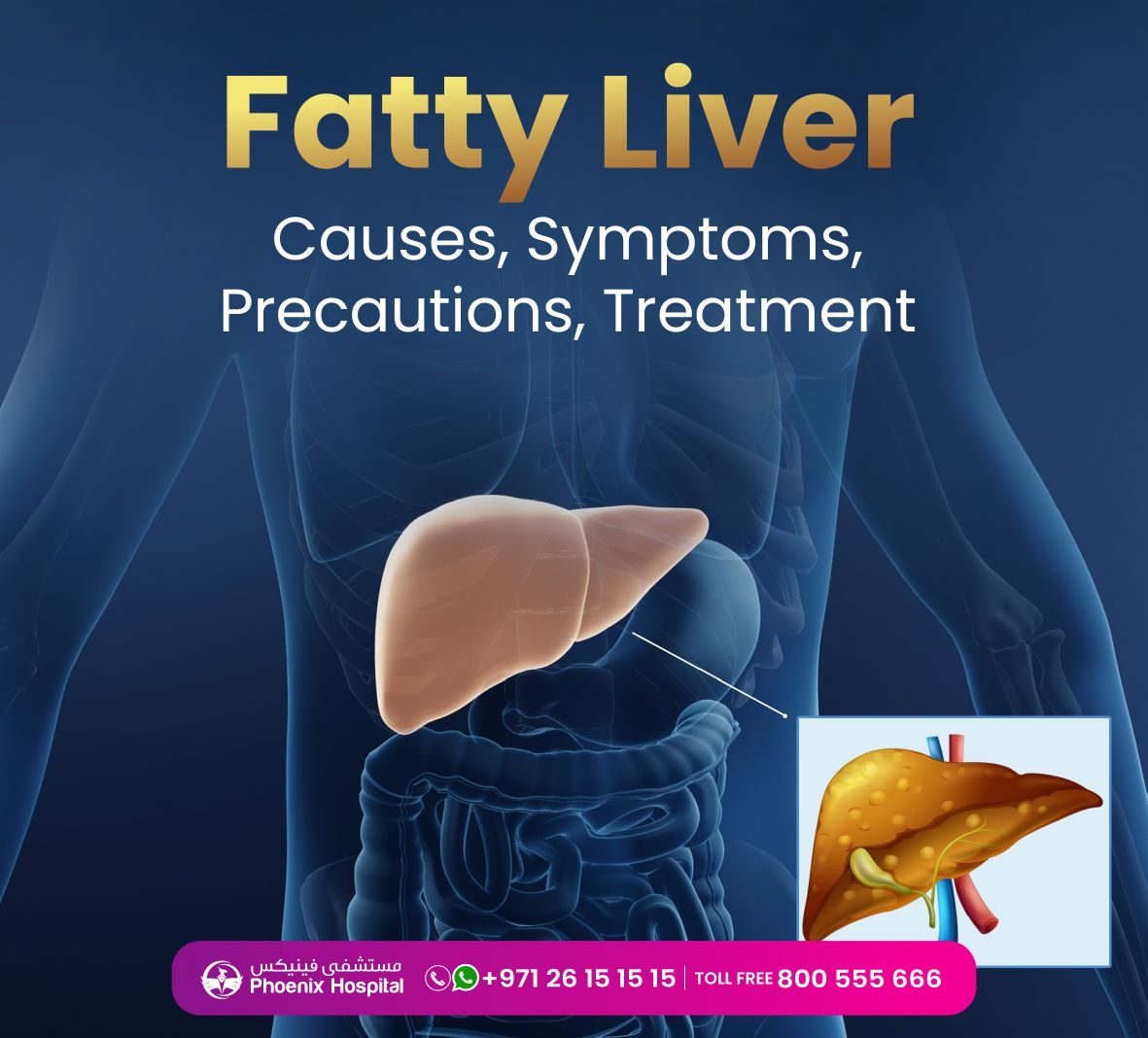
Fatty liver – symptoms, causes, and digestion

Is Sunset to Sunrise Method Proven for Weight loss

Circadian Rhythm and Its Influence on Our Eating Habits
Colon Cancer – Symptoms, Causes, & Treatment